life cycle of a seedless plant
Gametangia are prominent in seedless plants but are absent or rudimentary in seed plants. - produce gametes n through the process of mitosis.

Cyclic Electron Transport In Photosynthesis Photosynthesis Teaching Biology Electrons
Plant reproduction Other contents.

. Spores germinate forming a hapliod gametophyte. Seedless plants produce sperm equipped with flagella that enable them to swim in a moist environment to the archegonium. Terms in this set 17.
Haploid spores become haploid gametophytes. Seedless vascular plants still depend on water during fertilization as the flagellated sperm must swim on a layer of moisture to reach the egg. Pteridophytes ferns are the seedless vascular plants.
In seedless vascular plants the sporophyte became the dominant phase of the lifecycle. Some protists also have an alternation of generations life cycle but the structures that produce gametes in protists are usually single cells. Life cycle of seedless plant Life cycle of moss and fern ID.
Water is still required for fertilization of seedless vascular plants and most favor a moist environment. They have an alternation of generations not unlike the bryophytes the seedless nonvascular plants. Some plants such as fern or mosses produce different kinds of cells called Spores.
However not all plants produce seed. In seedless vascular plants such as ferns the sporophyte releases spores from the undersides of leaves. Seedless vascular plants reproduce through unicellular haploid spores instead of seeds.
- sperm cells are transported by water to egg cells. 2N stages - called alternation of generations or haplodiplontic life cycle-Reproduce mainly by sexual reproduction. The life cycle of seedless vascular plants alternates between a diploid sporophyte and a haploid gametophyte phase.
Seeds are considered to be a key adaptation for reproduction in a land habitat. Phylum Pterophyta Ferns As indicated in 1 of the website use the space below to draw a simple life cycle of the fern. In vascular plants the sporophyte generation is dominant.
The majority of living plants produce seeds and are divided into two large groups the gymnosperms and angiosperms. The diploid sporophyte is the dominant phase of the life cycle while the gametophyte is an inconspicuous but still-independent organism. The dominant part of the fern life cycle is the diploid sporophyte generation - those are the large plants that are obvious.
These plant does not produce seeds. The liverworts the hornworts and the mosses. Lab Assignment Seedless Vascular Plants Copy and pasting text is not allowed because doing so.
Gametophytes of seedless plants. Characteristics of Seedless Vascular Plants require water for fertilization sporophyte generation is dominant and only needs the gametophyte only in the early stages of development do not posses seeds they are vascularxylem and phloemvertical growth true plant organs. The diploid plant that produces spores is called a sporophyteThe haploid plant that produces gametes is called a gametophyte.
In seedless vascular plants the diploid sporophyte is the dominant phase of the life cycle. Remember that the moss life cycle is characterized by two types of haploid spores male and female. For every plant one of the two generations is usually dominant.
Ad Grow your Christian faith with a wide range of books from your favorite authors. The embryo is diploid therefore it becomes the sporophyte of the next generation. Recall the sporophytic generation is the diploid part of the life cycle and via meiosis haploid spores are produced.
Show reviews 1 Back to the top of the page. Modern-day seedless vascular plants include club mosses horsetails ferns. Everything Christian for Less.
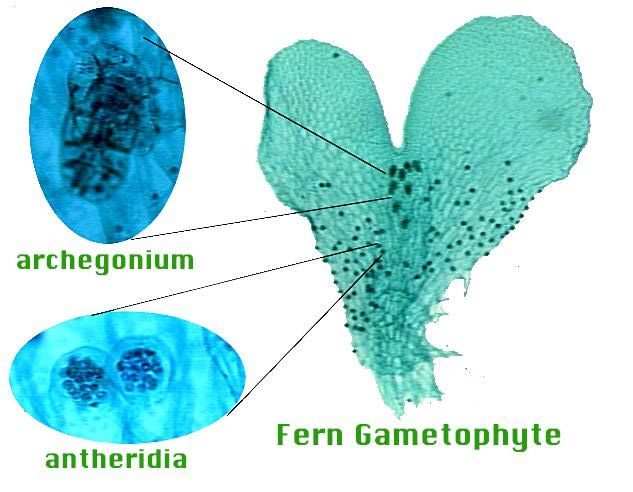
Include in the life cycle 2N N sporophyte gametophyte meiosis spores egg sperm antheridium archigonium fertilization sorus. 64 of people thought this content was helpful. Like all plants seedless vascular plants have a gametophytic generation and a sporophytic generation.
Haploid gametophytes go through mitosis to produce gametes reproductive cell with the haploid number of chromosomes Gametes combine during fertilization to produce a diploid sporophyte and the cycle repeats. Life cycle Add to my workbooks 5 Download file pdf Embed in my website or blog. The spores develop into tiny separate gametophytes from which the next generation of sporophyte plants grows.
The gametophyte is now less conspicuous but still independent of the sporophyte. The lightweight spores allow for easy dispersion in the wind. What Types of Plants Produce Seeds.
There are three main groups. They are collectively known as bryophytes. Seedless nonvascular plants are small.
View chapter 22 seedless vascular plantspdf from BIOLOGY 112 at Rowan-Cabarrus Community College. The fern life cycle illustrates sexual reproduction in the seedless vascular plants. The life cycle of seedless vascular plants is an alternation of generations where the diploid sporophyte alternates with the haploid gametophyte phase.
The dominant stage of the life cycle is the gametophyte. Without a vascular system and roots they absorb water and nutrients through all of their exposed surfaces. However in this life cycle the female gametophyte remained within the parental sporophytic tissue.
In seedless plants the fertilization and development of the next-generation sporophyte takes place separate from the first-generation sporophyte. The life cycle of a plant describes the different stages of the plant from the beginning of its life until the end which is from seed to mature plant. The embryo develops inside the archegonium as the sporophyte.
Zygote first cell formed from the fertilization of an egg cell with a sperm cell.

Ck 12 Foundation Biology Plants Plant Science Life Cycles

Plant Diversity Botany Plant Classification Plant Science

The Life Cycle Of A Fern Biology Plants Fern Life Cycle Spore

Life Cycle Of Seedless Vascular Plants Ehow Plants Vascular Plant Fern Plant

Bryophyte Life Cycle Stages Life Cycle Stages Plant Science Life Cycles

Middle Grades Plants Are At The Basis Of The Food Chain Where Would We Be Without Them And Look At That Diversity Biology Plants Teaching Plants Plants

Pin By Dandavats Dasa Flores On Botany Vascular Plant Development Faith

Fern Life Cycle Fern Life Cycle Plant Life Cycle Life Cycles

Plants Ii Non Vascular And Seedless Vascular Plants Biol110f2012 Confluence Vascular Plant Plants Vascular

The Life Cycle Of A Fern Plant Life Cycle Ferns Fern Life Cycle
Plant Family Tree Gymnosperms Plants With Cones Seedless Vascular Plants With Veins No Seeds Seedless Non Vas Plants Gymnosperm Evolution Of Plants

Life Cycle Of Seedless Vascular Plants Ck 12 Foundation Vascular Plant Life Cycles Vascular

Plant Morphology Diagram Google Search Ferns Plant Lessons Biology Drawing

Fern Plants And Their Life Cycle Seedless Vascular Updated Plants Fern Plant Ferns
Page Not Found Alternation Of Generations Biology Lessons Vascular Plant

Fern Life Cycle Worksheet Google Search Plant Science Teaching Plants Biology Notes

Lab Ch 16 Non Vascular Plants And Seedless Vascular Plants Biology 152 With Kinnes At Azusa Pacific University Studyblue Vascular Plant Vascular Plants

